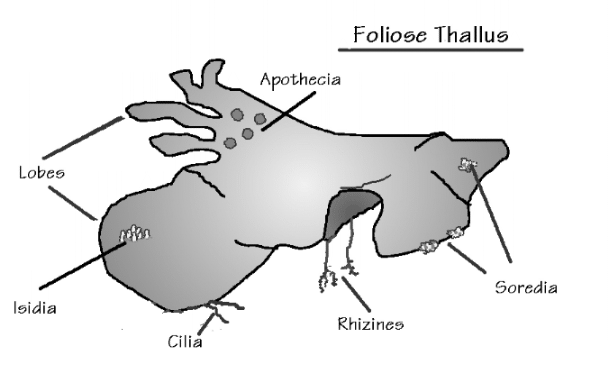
 A
A
Section A. Classification, Terminology and Life Cycles.
For questions 1 to 11, choose from the following list of major groups of fungi or fungal-like organisms.and ENTER the appropriate letter. (A - G)
B. Ascomycotina,
C. Zygomycotina,
D. Basidiomycotina - order Teliomycetes.
E. Chytridiomycota,
F. Basidiomycotina - order Holobasidiomycetes
G. Oomycetes
2. To which group does fungus B in Fig 1. belong ? ____________________
3. To which group does fungus C in Fig 1. belong ? ____________________
4. To which group does fungus D in Fig 1. belong ? ____________________
5. To which group does fungus E in Fig 1. belong ? ____________________
6. To which group does fungus F in Fig 1. belong ? ____________________
7. Group to which most lichen fungi belong ____________________
8. Group to which most wood-rotting fungi belong ____________________
9. Group to which the plant pathogenic rust and smut fungi belong _______________
10. Group to which potato late blight fungus belongs ____________________
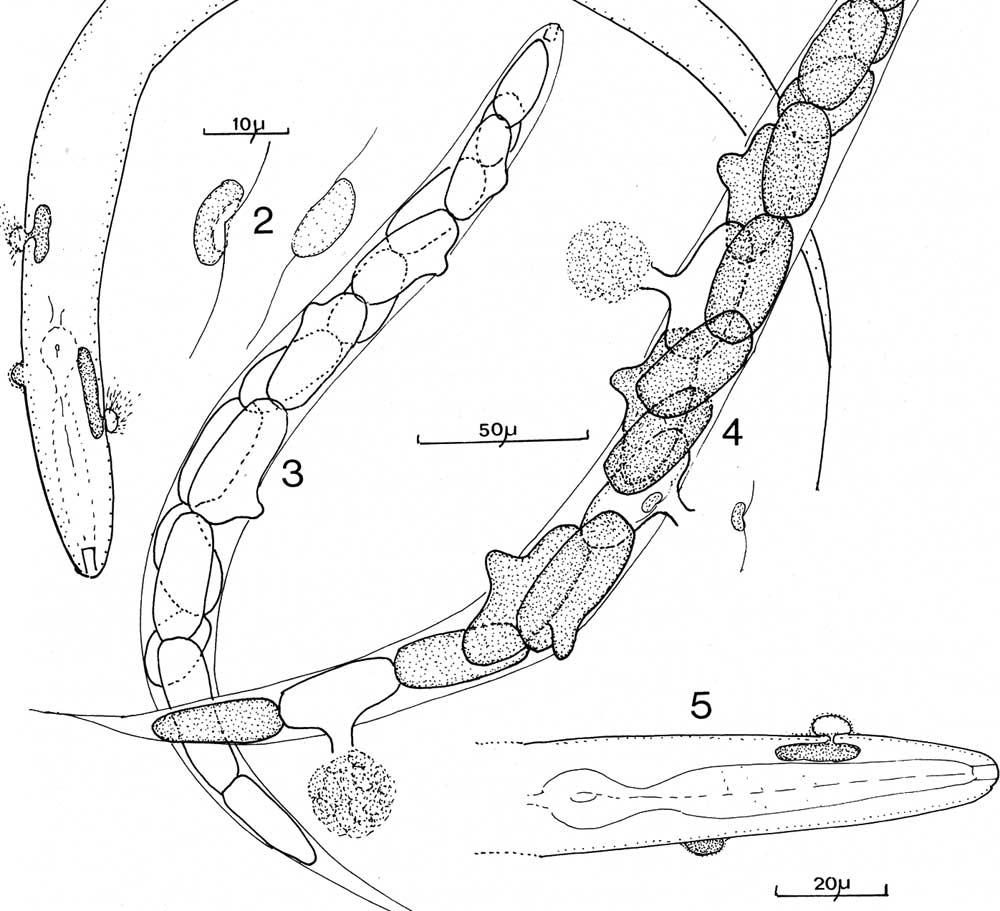
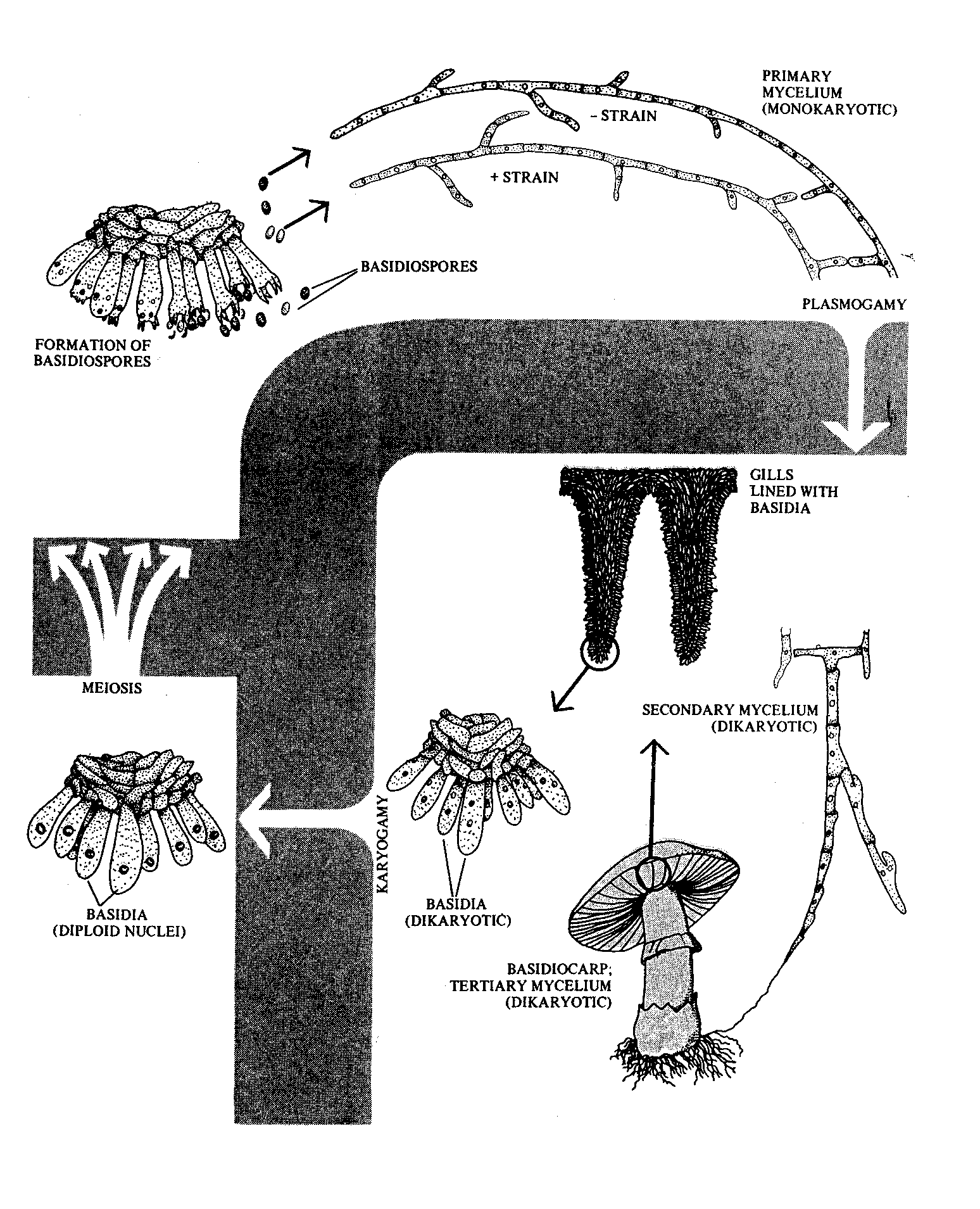
11. Group to which a fungus belongs which has no motile cells, wide, fast growing hyphae, with few or no septae, and which produces large numbers of asexually produced spores which are released from inside spherical ‘containers’ on stalks. _____________________
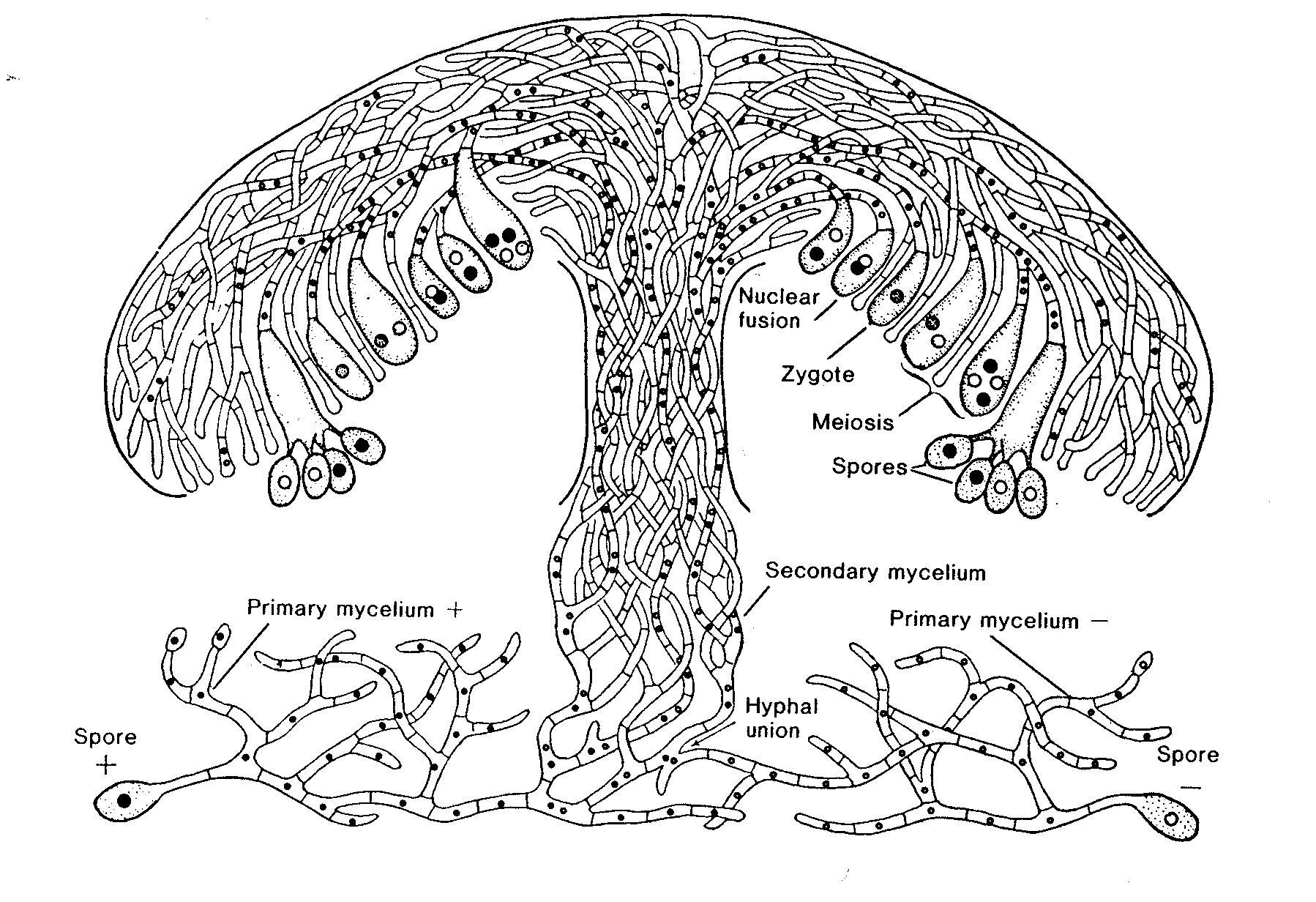
12. Many fungi produce tight knots of hyphae with a tough melanized outer surface, that are adapted to survival in harsh conditions e.g. winter. These structures are called ___________________________
13. Other fungi produce long cabled strands of hyphae, visible to the naked eye, also with a tough black (melanized) coat, which can spread underground for long distances. What are such structures called ? ___________________________
14. What is meant by anastomosis ? ___________________________________________
.FIGURE 1
 A
A
B
C (left) D (above)
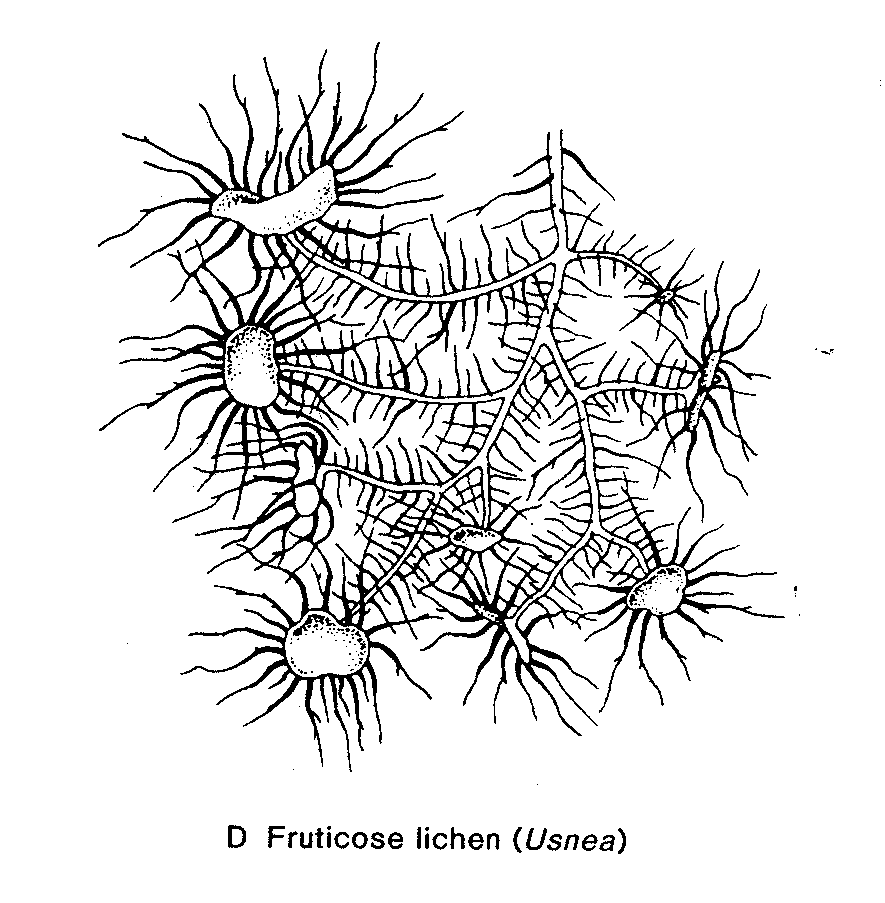 F
F
15. Zygomycetes produce asexual spores called sporangiospores,
while Ascomycetes (and some Basidiomycetes) produce asexual spores called
conidia. What is the key difference between these 2 types? ___________________________________________________________________
16. What is a Deuteromycete ? ______________________________________________________
17. What kind of sexual spore is produced by Zygomycetes ? ___________________________
18. What kind of sexual spore is produced by Oomycetes ? ___________________________
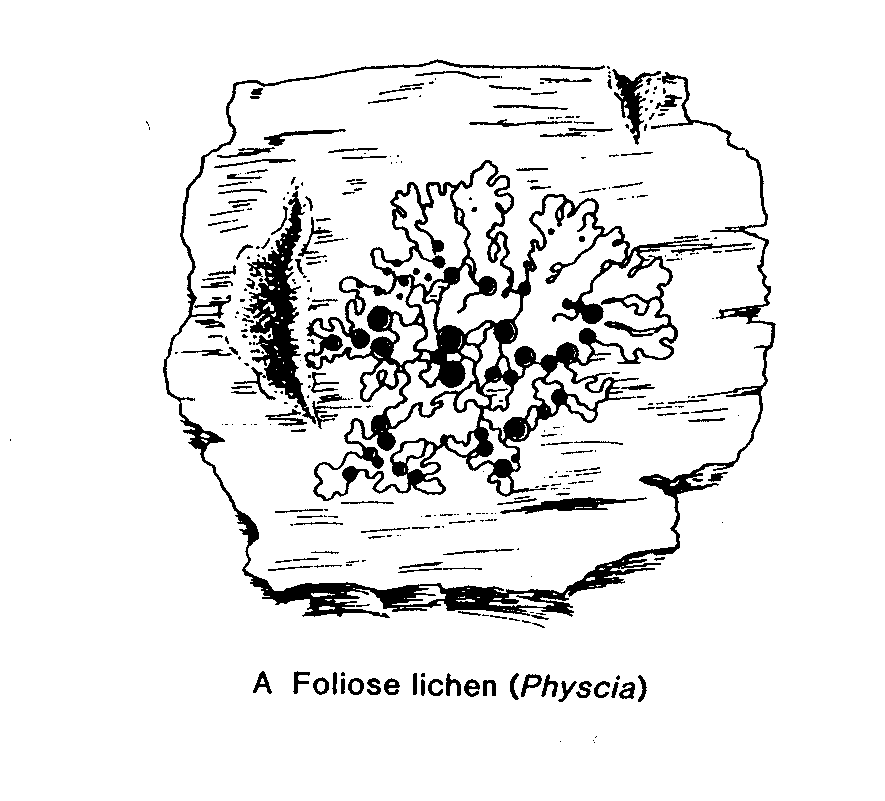
19. What group does the fungus shown below belong to _______________(choose from the list at the top of this section)
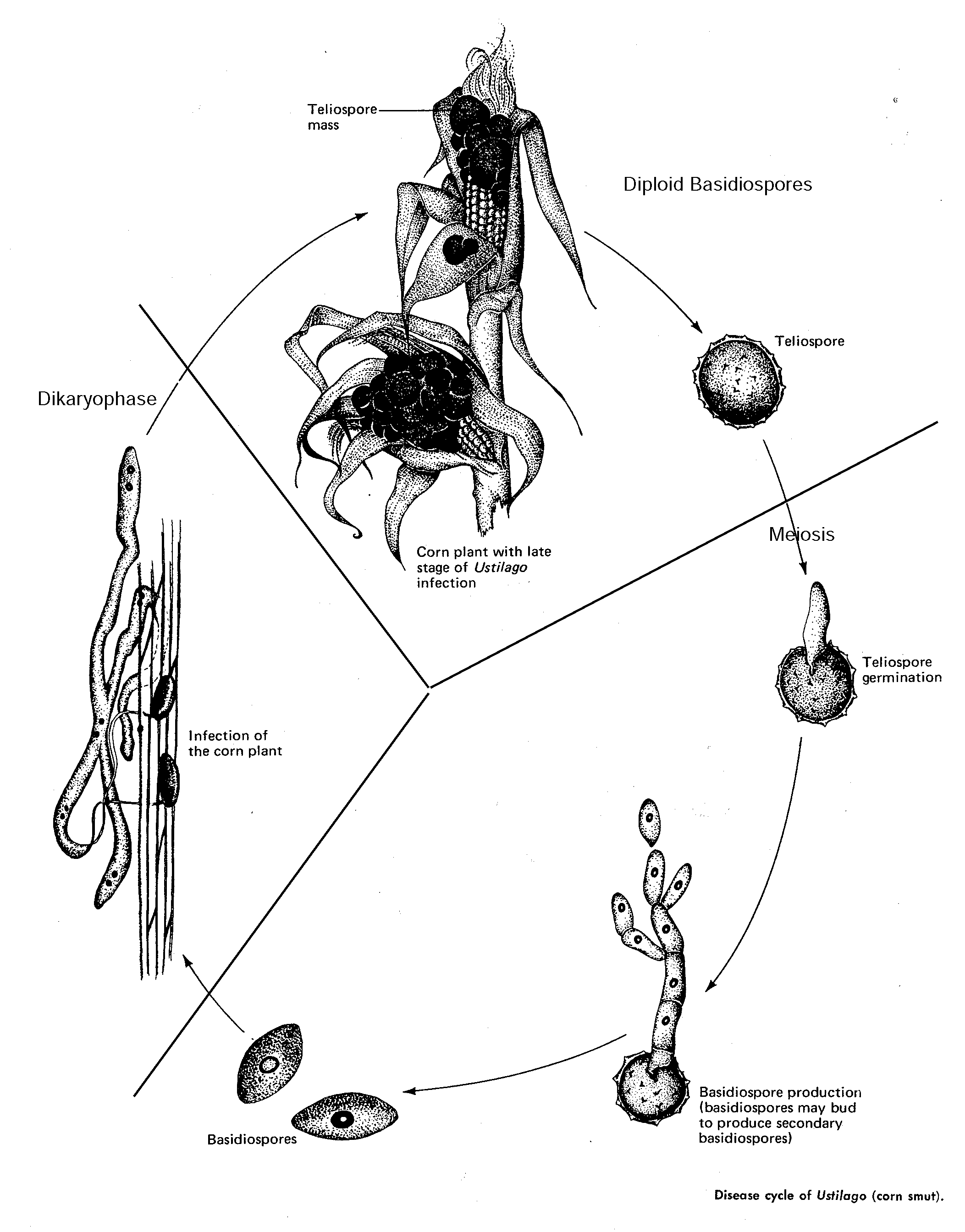
20. The life cycle below is typical of the group __________________________
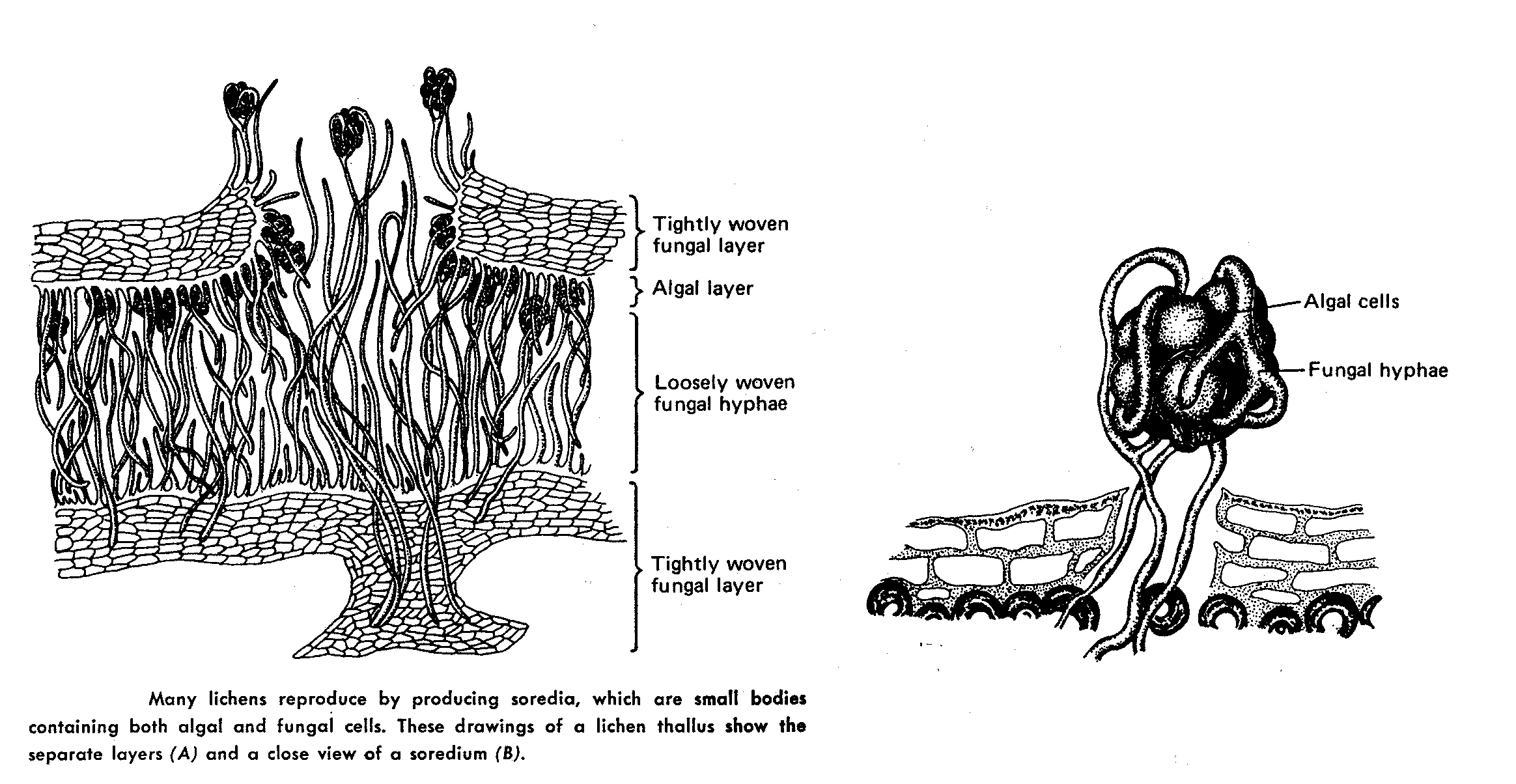
21. Most lichens produce sexual spores in structures called (circle correct one)
a) apothecia
b) podetia
c) gleba
d) soredia
e) isedia
22. Fungi which grow in the shoots of plants without causing any apparent ill-effects or disease symptoms on the host are called ___________________________________________________
23. Asexually produced reproductive structure in lichens which contains both phycobiont and mycobiont ____________________________________________________________________
24. The phycobiont component of a lichen is most often a member of the ______ ___________
25. Lichens are useful indicators of (circle best one) :-
a) rain-borne pollutants
c) global warming
d) density of people
e) a very dry environment
27. What benefits does the fungus partner in mycorrhizae obtain from the relationship? _______________________________________________________________________________
28. What benefits does the plant partner in mycorrhizae obtain from the relationship? _______________________________________________________________________________
29 – 33. Complete the following table to show the differences between
ectomycorrhizae and endomycorrhizae
| Taxonomic Group of fungus | Type of plant (woody or non-woody) | Hartig Nets (y/n); | arbuscules (y/n) | penetration of root cells (y/n) | |
| Ectomycorrhizae | |||||
| Endomycorrhizae |
34. The term ‘mantle’ when applied to mycorrhizae, describes
___________________________________________________
35 and 36. Yeasts are a diverse group with representatives in several of the major taxonomic groups of fungi. Two of the main groups are Ascomycetes and Basidiomycetes. Yeasts in these 2 groups can be distinguished on the basis of :-
(circle best TWO of the following )
b) both form buds but differ in the underlying mechanism
c) only Ascomycetes form buds; Basidiomycetes divide by fission
d) type of glucan in the walls
e) only the Basidiomycete yeasts have sexual stages.
a) cells which divide by a fission-type of mechanism
b) 8-spored asci
c) long basidiospores
d) long ascospores
e) huge, thick walled spores
(circle TWO)
b). it is able to convert sugars to alcohol under aerobic conditions
c). it is able to convert sugars to alcohol under anaerobic conditions.
d). it is able to convert alcohol to CO2 so producing a ‘fizzy’ liquid.
e) it can tolerate relatively high concentrations of alcohol
42-45. Give the appropriate term for each of the following :-
(choose form: symbiosis, pathogen, parasite, saprotroph, )
42. Association of two different organisms living in close physical contact ______________
43. An organism that derives part or all of its food from another _____________
44. An organism [or abiotic agent] that causes disease _____________
45. Association of two different organisms that is beneficial to both partners ___________
46. Name an animal (non-human) which cultivates fungi in ‘gardens’ ______________
47. In the parasexual cycle, once a somatic diploid nucleus has formed, it continues to divide by mitosis. Sometimes new ‘sectors’ of the fungus arise following these mitotic divisions which express new phenotypes.
These appear to arise by 2 mechanisms; one of which is ________________________________
48. The theory which describes the inter-relationship between the major genes for resistance in plants and those for virulence in fungi is called _________________________________
49. A mutant fungus is found which shows the following growth patterns on media which involve various combinations of the three growth factors, lysine (L), histidine (H) and methionine (M) added to a minimal medium (MM)
No growth ………. MM alone; MM + L + H; MM + M + H
Growth ……………MM + L +M; MM + L + M + H
This strain is therefore of genotype ……. lys his met (fill in ‘+’ or ‘–‘ symbols for each gene as appropriate)
50. Most yeast strains are heterothallic; however, those strains that have the dominant allele HO are homothallic because ______________________________________________________
51. When a cross is made between a fungus that is wild-type and one that carries 2 auxotrophic alleles, arg- and his -, the progeny are found to be as follows:-
52. Using the above data, what % of these progeny would grow on minimal medium supplemented with histidine ? ______________________________________________________
53. What formula is used to calculate the distance of a gene from its centromere ? __________
54. One or more of the asci shown below provide evidence for models of crossing-over which predict heteroduplex DNA (DNA which has one helix derived from one parental DNA molecule and one from the other parent DNA mol.). Which is it/ are they ? – circle the corresponding letters
A B C D E F G H
55. What is a haustorium _________________________________________________________
56. A phytotoxin is a compound produced during some fungal diseases. It is synthesized by the ________________ and has a destructive effect on the ______________________.
57. A phytoalexin is a compound produced during some fungal diseases. It is synthesized by the ________________ and has a destructive effect on the ______________________.
58. Some hosts are resistant to their fungal pathogen because the cells that are initially infected immediately die and so prevent further spread. This is a called a _________________________
59. Dr. Dobinson described research on which fungus ? ________________________________
60. Forecasting the development of an epiphytotic requires models based on these 4 key factors: host susceptibility, pathogen virulence, environmental factors and time. This interplay of factors is called _____________________________________________
D. Importance of Fungi.
61. Give an example of an important fungal product that is highly toxic to humans. __________________________________
62. Give an example of an important fungal product that is hallucinogenic.
__________________________________
64. Give an example of an important fungal product that is used as an immunosuppressant. __________________________________
65. What genus of fungus produces compounds that were historically important as toxins in food products but are now used as both medicinal and ‘street’ drugs.
__________________________________
66 – 78. For each fungus in List A, select the description in List B which is most appropriate for that species. Enter the corresponding LETTER in the blank.
LIST A.
66. Ustilago _________
67. Synchytrium _________
68. Penicillium _________
69. Trichophyton_________
70. Armillaria _________
71. Pisolithus _________
72. Pleurotus _________
73. Rhizopus _________
74. Aspergillus _________
75. Plasmodiophora_______
76. Neurospora _________
77. Amanita _________
78. Puccinia _________
LIST B.
A. Important for research into meiosis and recombination
B. Causes ringworm or tinea in humans
C. Causes bread mould
D. Source of the most poisonous fungal toxin known
E. Causes diseases called ‘smuts’
F. Causes diseases called ‘rusts’
G. Causes a ‘wart’ disease of potatoes
H. Causes ‘club root’ of cabbage
J. Important in making blue cheese
K. Important parasite of trees.
L. Source of aflatoxins
M. Edible fungus that is an important parasite of nematodes
N. Important ectomycorrhizal fungus
O. Important disease of peaches
79. What role do fungi play in forests apart from being important pathogens and mycorrhizal partners ? _______________________________________________
80. Some human fungal diseases become established below the skin
or are systemic. Give an example (name of disease or genus of fungus) _______________________________________