Student # _____________
Name: ________________
The University of Western Ontario
London, Canada
Biology 318b, Biology of Fungi
Midterm Test
Feb 18, 2002 2-4 pm
25 % of Final Mark
This Exam paper is composed of 4 sections and covers 6 sides plus this cover page.
Please ensure that it is complete.
All answers are to be entered directly on the exam.
Each question worth 1 mark unless otherwise indicated. Perfect mark = 75
Total = ____ out of 75
Please use the space below to indicate any concerns or ambiguities about any questions
SECTION A. CLASSIFICATION.
For questions 1 to 15 , choose from the following list of major groups of fungi or fungal-like organisms.and ENTER the appropriate letter. (A - G)
A. Slime moulds,
B. Ascomycotina,
C. Zygomycotina,
D. Basidiomycotina - order Teliomycetes.
E. Chytridiomycota,
F. Basidiomycotina - order Holobasidiomycetes
G. Oomycetes
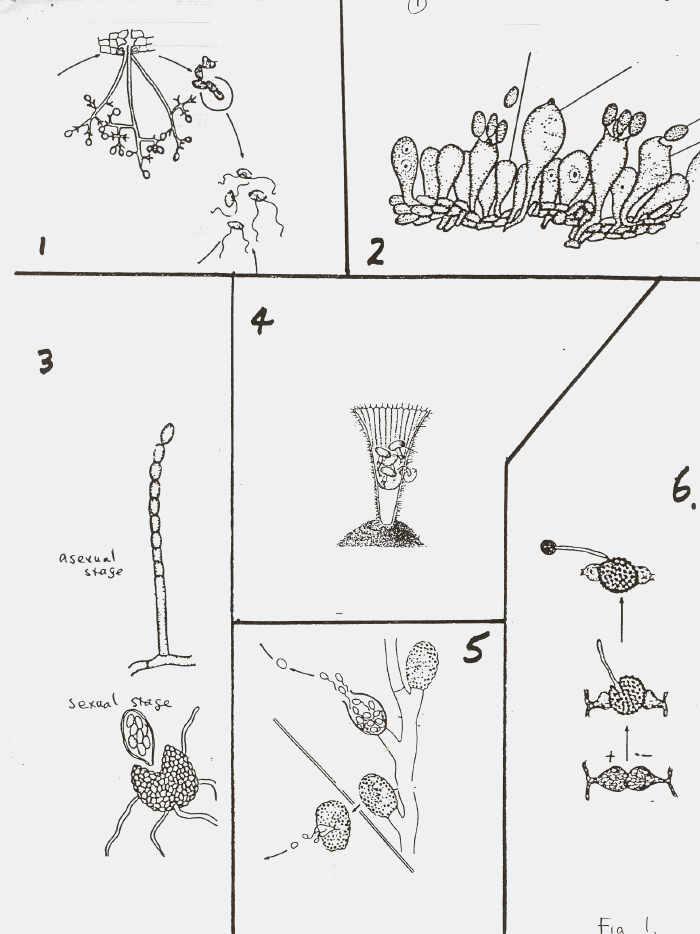
1. To which group does fungus # 1 in Fig 1. belong ? ____________________
2. To which group does fungus # 2 in Fig 1. belong ? ____________________
3. To which group does fungus # 3 in Fig 1. belong ? ____________________
4. To which group does fungus # 4 in Fig 1. belong ? ____________________
5. To which group does fungus # 5 in Fig 1. belong ? ____________________
6. To which group does fungus # 6 in Fig 1. belong ? ____________________
7. Group to which most lichen fungi belong ____________________
8. Group to which most wood-rotting fungi belong ____________________
9. Group to which the plant pathogenic rust and smut fungi belong ____________________
10. Which group of fungi can produce closed structures called
cleistothecia which contain the sexual spores and spore bearing cells? _______________________

11. Which group of fungi includes those which can form amoebae ? _____________________
12. Which group of fungi are non-motile and have coenocytic cells ? _____________________
13. Which group of fungi includes those that can be macrocyclic ? ___________________
14. Which group of fungi includes yeasts that bud enteroblastically ? ______________
15. Which group of fungi can produce their sexual spores in operculate containers? ___________
Section B. TERMINOLOGY
Q 16 -30. For each term in List A select the description in List B that is the MOST
APPROPRIATE for this term. Enter the corresponding number in the blank [if appropriate you can use the same number more than once].
LIST A. .
16. hymenium __________
17. isedia __________
18. perithecium __________
19. oogonium __________
20. aseptate __________
21. anamorph __________
22. ascoma __________
23. homothallic __________
24. chitin __________
25. basidium __________
26. stipe __________
27. spermatia __________
28. rhizomorph __________
29. volva __________
30. aecia __________
LIST B
1. sexual cell bearing spores (products of meiosis) on its outside
2. has 2 mating type genes - each usually with many alleles
3. the female sexual structure in some fungi
4. term for a fungus-root partnership
5. having no cross-walls in hyphae
6. small uninucleate haploid spores produced by rust fungi
7. sexual cell bearing spore products of meiosis inside it
8. cup-like structure at base of a mushroom
9. polysaccharide compound found in fungal cell walls
10. term describing the sexual stages of an organism
11. term describing the asexual stages of an organism
12. root-like structure produced by some fungi
13. requiring 2 different individuals to initiate mating
14. capable of mating as a single individual
15. fruit body in Ascomycotina
16. ‘stalk’ of mushroom
17. vegetative reproductive structure in a lichen
18. structure with narrow opening; containing asci
19. dikaryotic spore-producing lesions on Barberry.
20. lichen growth form that is ‘leaflike’
21. black ‘bootlace-like’ structure
22. asexually produced spore
23. fertile spore bearing surface
31. Name for fungal Kingdom which includes the Omycetes __________________________
32. Cup-shaped fruit body in Ascomycetes __________________________
33. asexual spore produced by Zygomycetes _________________________
34. diploid spore produced by smut fungi ______________________
35. name for type of flagellum which carries fine side hairs or mastigonemes _____________________
36. name for algal partner in a lichen ____________________
37. group of Ascomycetes for which no teleomorphs are known _______________________
38. asexual spore produced by Ascomycetes __________________________
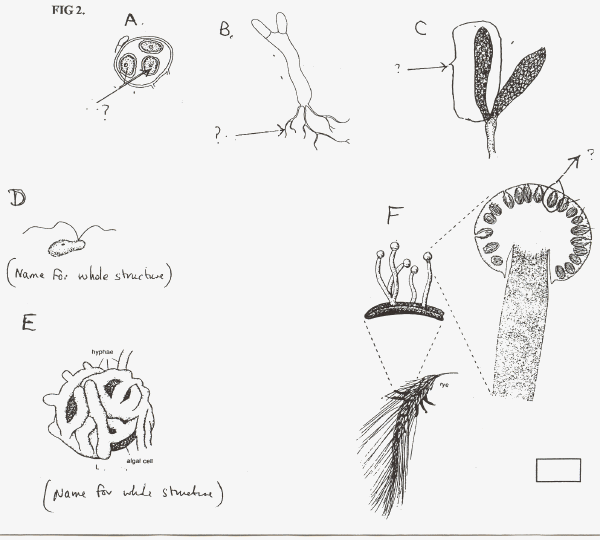
Q 39 - 44. Identify the structures labelled in Fig 2 below.
39. The structure in Fig 2 - A = ______________________________________
40. The structure in Fig 2 - B = ______________________________________
41. The structure in Fig 2 - C = ______________________________________
42. The structure in Fig 2 - D = ______________________________________
43. The structure in Fig 2 - E = ______________________________________
44. The structure in Fig 2 - F = ______________________________________
Section C. LIFE CYCLE
Q. 45 - 51. For each of the following say whether the nuclei are diploid (2n), haploid (1n) or dikaryotic(n+n)
45) zygospore ............................................................ _______________
46) normal spreading mycelium of a Basidomycete............................ _______________
47) normal spreading mycelium of an Ascomycete............................_______________
48) uredospore . ................................................ _______________
49) nucleus in an antheridium ...................................... _______________
50) young ascus just prior to nuclear division.. ...................................._______________
51) hyphae of an Oomycete . ................................ ....._______________
52. Draw below the life cycle of a typical Zygomycete showing details of both asexual and sexual
reproduction. (5 marks)
53. Complete the lables in the diagram of the life cycle below (6 marks)
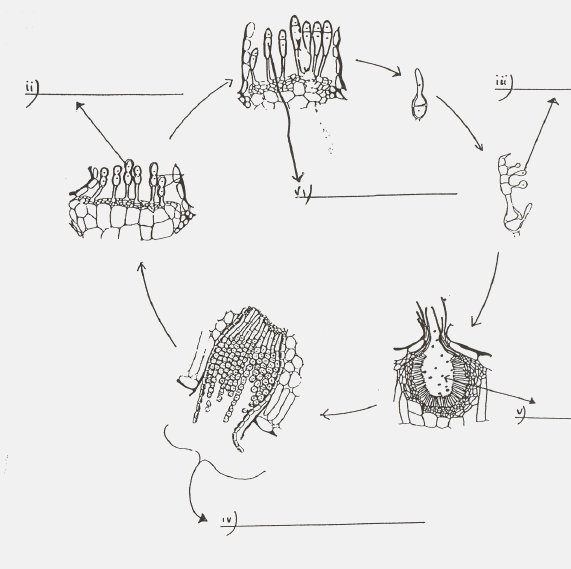
54. Indicate on the above life cycle which host species are being attacked.
Section D. Economic Importance.
Q 55 -66 For each question in List A select the fungal genus in List B that is the MOST APPROPRIATE. Enter the corresponding number in the blank [if appropriate you can use the same number more than once].
LIST A.
55. Fungus important in wine making. _______
56. Produces highly toxic compounds. _______
57. Important in making ‘blue’ cheese. _______
58. Important parasite of trees _______
59. May spoil bread _______
60. Important for genetics research. _______
61. Caused major social changes in Ireland ______
62. Causes ‘thrush’ disease in humans. _______
63. Causes potato wart disease . _______
64. Cause of mediaeval outbreaks of madness/death _______
65. Cause of corn smut _______
66. Very expensive edible Basidiomycete _______
LIST B.
1. Claviceps
2. Armillaria
3. Agaricus
4. Synchytrium
5. Allomyces
6. Neurospora
7. Penicillium
8. Phytophthora
9. Rhizopus
10. Ustilago
11. Candida
12. Amanita
13. Saccharomyces
14. Tuber
15. Morchella