CH310M/318M Organic I
|
Dr. Brian
Pagenkopf |
|
|
|
Hydrogen Bonding In Alcohols.
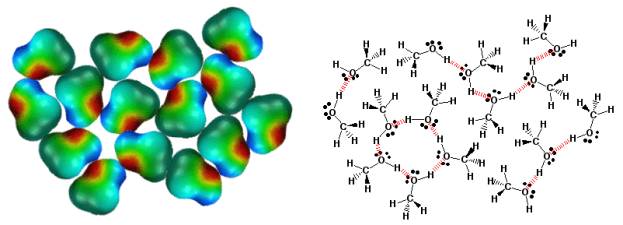
Alcohols have relatively high boiling points because the molecules stick together due to hydrogen bonding. Hydrogen bonding occurs when the hydrogen atoms attached to N, O, or S atoms interact with the lone pairs of electrons on N, O, or S atoms. This is really an electrostatic interaction in that the hydrogen atoms possess a partial positive charge are thus attracted to the partial negative charge of the electronegative N, O, or S atoms. For calibration, hydrogen bonds are worth about 1-4 kcals/mol. Hydrogen bonds are extremely important in almost all aspects of biochemistry and biology. In the above 2-dimensional illustration, notice how the alcohol molecules are arranged to produce the maximum amount of hydrogen bonding. Hydrogen bonds are indicated as red dashed lines in the schematic on the right.
Hydrogen bonding allows proton transfers to occur very rapidly because the protons are already ‘shared’ between more than on Lewis Basic oxygen atom.