
Quiz 9
Perform a bivariate regression on the following data (17 marks)
| River | length/1000 | discharge/10 | length*discharge | length2 | discharge2 |
| Nile | 6.7 | 32.4 | 216.8 | 44.8 | 1049.8 |
| Zaire (Congo) | 4.4 | 125 | 546.4 | 19.1 | 15625 |
| Niger | 4.2 | 31 | 129.7 | 17.5 | 961 |
| Zambezi | 2.7 | 15 | 41 | 7.5 | 225 |
| Orange | 2.1 | 0.9 | 1.9 | 4.4 | 0.8 |
| Chang Jiang (Yangtze) | 5.8 | 90 | 521.7 | 33.6 | 8100 |
| Ob | 5.6 | 43.1 | 239.9 | 31 | 1857.6 |
| Huang Ho (Yellow) | 4.7 | 5 | 23.3 | 21.8 | 25 |
| Yenisei | 4.5 | 60 | 270.4 | 20.3 | 3600 |
| total= | 40.6 | 402.4 | 1991.1 | 199.9 | 31444.2 |
| mean= | 4.5 | 44.7 | 221.2 | 22.2 | 3493.8 |
Calculate the regression variance (3 marks)
| x | y | x*y | |||
| River | length/1000 | discharge/10 | length*discharge | length2 | discharge2 |
| Nile | 6.7 | 32.4 | 216.8 | 44.8 | 1049.8 |
| Zaire (Congo) | 4.4 | 125 | 546.4 | 19.1 | 15625 |
| Niger | 4.2 | 31 | 129.7 | 17.5 | 961 |
| Zambezi | 2.7 | 15 | 41 | 7.5 | 225 |
| Orange | 2.1 | 0.9 | 1.9 | 4.4 | 0.8 |
| Chang Jiang (Yangtze) | 5.8 | 90 | 521.7 | 33.6 | 8100 |
| Ob | 5.6 | 43.1 | 239.9 | 31 | 1857.6 |
| Huang Ho (Yellow) | 4.7 | 5 | 23.3 | 21.8 | 25 |
| Yenisei | 4.5 | 60 | 270.4 | 20.3 | 3600 |
| total= | 40.6 | 402.4 | 1991.1 | 199.9 | 31444.2 |
| mean= | 4.5 | 44.7 | 221.2 | 22.2 | 3493.8 |
| b= | 10.49794348 | ||||
| a= | -2.540745655 | ||||
| regression variance | |||||
| River | y hat | y hat sq | |||
| Nile | 67.79547565 | 4596.226519 | |||
| Zaire (Congo) | 43.65020565 | 1905.340453 | |||
| Niger | 41.55061696 | 1726.453769 | |||
| Zambezi | 25.80370174 | 665.8310234 | |||
| Orange | 19.50493565 | 380.4425147 | |||
| Chang Jiang (Yangtze) | 58.34732652 | 3404.410512 | |||
| Ob | 56.24773783 | 3163.808011 | |||
| Huang Ho (Yellow) | 46.7995887 | 2190.201502 | |||
| Yenisei | 44.7 | 1998.09 | |||
| total | 404.3995887 | 20030.80431 | |||
| s sq= | 227.5549228 | ||||
| sy sq | 1495.71 | ||||
| r sq= | 0.152138398 | ||||
Quiz 8
Determine the correlation coefficient between a riverís length and its
discharge. (15) marks
Test the significance of r. (5 marks)
| River | length | discharge |
| Nile | 6690 | 324 |
| Zaire (Congo) | 4371 | 1250 |
| Niger | 4184 | 310 |
| Zambezi | 2736 | 150 |
| Orange | 2092 | 9 |
| Chang Jiang (Yangtze) | 5797 | 900 |
| Ob | 5567 | 431 |
| Huang Ho (Yellow) | 4667 | 50 |
| Yenisei | 4506 | 600 |
Extra Credit (2 marks)
What is the Spearmanís correlation coefficient for the above data?
| x | y | xy | x sq | y sq | ||
| River | length | discharge | ||||
| Nile | 6690 | 324 | 2167560 | 44756100 | 104976 | |
| Zaire (Congo) | 4371 | 1250 | 5463750 | 19105641 | 1562500 | |
| Niger | 4184 | 310 | 1297040 | 17505856 | 96100 | |
| Zambezi | 2736 | 150 | 410400 | 7485696 | 22500 | |
| Orange | 2092 | 9 | 18828 | 4376464 | 81 | |
| Chang Jiang (Yangtze) | 5797 | 900 | 5217300 | 33605209 | 810000 | |
| Ob | 5567 | 431 | 2399377 | 30991489 | 185761 | |
| Huang Ho (Yellow) | 4667 | 50 | 233350 | 21780889 | 2500 | |
| Yenisei | 4506 | 600 | 2703600 | 20304036 | 360000 | |
| total | 40610 | 4024 | 19911205 | 199911380 | 3144418 | |
| mean | 4512.222 | 447.1111 | ||||
| sx= | 1360.965 | |||||
| sy= | 386.6154 | |||||
| r= | 0.370396 | |||||
| t= | 1.055016 | |||||
| x | y | x rank | y rank | d | d sq | |
| River | length | discharge | ||||
| Nile | 6690 | 324 | 1 | 5 | -4 | 16 |
| Zaire (Congo) | 4371 | 1250 | 6 | 1 | 5 | 25 |
| Niger | 4184 | 310 | 7 | 6 | 1 | 1 |
| Zambezi | 2736 | 150 | 8 | 7 | 1 | 1 |
| Orange | 2092 | 9 | 9 | 9 | 0 | 0 |
| Chang Jiang (Yangtze) | 5797 | 900 | 2 | 2 | 0 | 0 |
| Ob | 5567 | 431 | 3 | 4 | -1 | 1 |
| Huang Ho (Yellow) | 4667 | 50 | 4 | 8 | -4 | 16 |
| Yenisei | 4506 | 600 | 5 | 3 | 2 | 4 |
| total | 64 | |||||
| r= | 0.466667 | |||||
| t= | 1.396017 |
Quiz Seven
There are 4 neighbourhoods sampled with housing prices recorded in each.
Determine if there is a difference in the mean housing price of homes in the
neighbourhoods.
Provide the hypotheses and all relevant calculations. Use α=.05.
| neighborhood | price |
| 1 | 175 |
| 1 | 147 |
| 1 | 138 |
| 1 | 156 |
| 1 | 184 |
| 1 | 148 |
| 2 | 151 |
| 2 | 183 |
| 2 | 174 |
| 2 | 181 |
| 2 | 193 |
| 2 | 205 |
| 2 | 196 |
| 3 | 127 |
| 3 | 142 |
| 3 | 124 |
| 3 | 150 |
| 3 | 180 |
| 4 | 174 |
| 4 | 182 |
| 4 | 210 |
| 4 | 191 |
| House prices by Neighborhood | |||||||
| Ho: There is no difference between the mean house prices by neighborhood | |||||||
| H1: The is a difference in the mean prices by neighborhood | |||||||
| df between=3 | df within=18 | ||||||
| df=3,df=18 | p.05=?, p.01=? | reject the null | |||||
| neighborhood | price | x2 | zone | price | |||
| 1 | 175 | 30625 | 1 | 175 | |||
| 1 | 147 | 21609 | T= | 3711 | 1 | 147 | |
| 1 | 138 | 19044 | sum x sq | 638941 | 1 | 138 | |
| 1 | 156 | 24336 | 1 | 156 | |||
| 1 | 184 | 33856 | 1 | 184 | |||
| 1 | 148 | 21904 | 1 | 148 | |||
| 2 | 151 | 22801 | sum sample 1 | 948 | 149784 | ||
| 2 | 183 | 33489 | 2 | 151 | |||
| 2 | 174 | 30276 | 2 | 183 | |||
| 2 | 181 | 32761 | 2 | 174 | |||
| 2 | 193 | 37249 | 2 | 181 | |||
| 2 | 205 | 42025 | 2 | 193 | |||
| 2 | 196 | 38416 | 2 | 205 | |||
| 3 | 127 | 16129 | 2 | 196 | |||
| 3 | 142 | 20164 | sum sample 2 | 1283 | 235155.6 | ||
| 3 | 124 | 15376 | 3 | 127 | |||
| 3 | 150 | 22500 | 3 | 142 | |||
| 3 | 180 | 32400 | 3 | 124 | |||
| 4 | 174 | 30276 | 3 | 150 | |||
| 4 | 182 | 33124 | 3 | 180 | |||
| 4 | 210 | 44100 | sum sample 3 | 723 | 104545.8 | ||
| 4 | 191 | 36481 | 4 | 174 | |||
| sum | 3711 | 638941 | 4 | 182 | |||
| 1/nT2 | 625978.2273 | 4 | 210 | ||||
| SST= | 12962.77 | 4 | 191 | ||||
| sum sample 4 | 757 | 143262.3 | |||||
| sum Ti2= | 632747.6 | ||||||
| SSR= | 6769.394 | ||||||
| SSE=SST-SSR | |||||||
| SSE= | 6193.379 | ||||||
| MSR= | 2256.465 | ||||||
| MSE= | 344.0766 | ||||||
| f=MSR/MSE | 6.55803 | ||||||
Quiz Six
Geography 301a, 2005
1. Complete the following table if it is known that there are 3 samples with
sizes 5, 7 and 7 respectively. (10 points)
| Source of Variation | Sum of Squares | Degrees of Freedom | Mean Square | Test Statistics |
| Treatments | 23.45 | 2 | 11.725 | |
| Error | 100 | 16 | 6.25 | F=1.88 |
| Total | 123.45 | 18 | ||
What is your conclusion about differences between the means?
Critical value is 3.63 so we conclude there in no
differences between the means
2. Analysis of variance results are not affected in each of the following cases,
please explain why this is true in each case. (2 points each)
a) The same constant is added to every sample score.
Variance is a measure of spread of the data so adding a
constant to each value will not change that
b) The order of the samples is changed.
The order of the samples isnít used in the calculations so
its irrelevant
3. What was the case study about in the significance test video? (4 points)
Shakespeare
4. Circle the letter of the correct formula for straight line distance. (2
points)
equation b is correct
Quiz 5
Geography 301a, 2005
1. What is Simpsonís paradox? (4 marks)
The direction of an association can be reversed by a
lurking variable
2. What product was tested in the video on t tests with the pairwise t test?(2
marks)
Nutrasweet in pop
3.Determine whether the point pattern in the map below is random or not (14
points).
Use a t-test.
| cell count (xi) | fi | x sq | fxsq | fx | fx sq/36 |
| 5 | 1 | 25 | 25 | 5 | |
| 4 | 1 | 16 | 16 | 4 | |
| 3 | 2 | 9 | 18 | 6 | |
| 2 | 2 | 4 | 8 | 4 | |
| 1 | 8 | 1 | 8 | 8 | |
| sums | 14 | 75 | 27 | 20.25 | |
| var= | 1.564286 | vmr= | 2.085714 | ||
| mean= | 0.75 | ||||
| numerator | 1.085714 | 4.541869 | t value | ||
| denominator | 0.239046 |
conclusion not random
Quiz 4
Geography 301a, 2005
1. A pair of cases is concordant if the value of each variable is larger (or
smaller) for one case than for the other case.
Variable 1 Variable 2
| Variable 1 | Variable 2 | ||
| case 1 | 5 | 4 | |
| case 2 | 4 | 3 | |
| case 3 | 4 | 2 |
For each of the pairs of cases identify which are
concordant if any , which are disconcordant if any and which are tied, if any.
(3 marks)
cases 1,2 ____________
cases 1,3 ____________
cases 2,3____________
Case 1,2 is concordant
case 1,3 is concordant
case 2,3 is tied
2. Determine whether the 3 colored dice are fair using chi square (6 marks)
Using theory o-e sq o-e sq/e
| Die/ Value | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | Total |
| Blue | 10 | 15 | 30 | 30 | 15 | 20 | 120 |
| Red | 12 | 20 | 35 | 30 | 3 | 20 | 120 |
| Green | 17 | 17 | 21 | 20 | 26 | 19 | 120 |
| Total | 39 | 52 | 86 | 80 | 44 | 59 | 360 |
| Using theory | o-e | sq | o-e sq/e | |||
| 1 | 1 | 10 | 20 | -10 | 100 | 5 |
| 1 | 2 | 15 | 20 | -5 | 25 | 1.25 |
| 1 | 3 | 30 | 20 | 10 | 100 | 5 |
| 1 | 4 | 30 | 20 | 10 | 100 | 5 |
| 1 | 5 | 15 | 20 | -5 | 25 | 1.25 |
| 1 | 6 | 20 | 20 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 2 | 1 | 12 | 20 | -8 | 64 | 3.2 |
| 2 | 2 | 20 | 20 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 2 | 3 | 35 | 20 | 15 | 225 | 11.25 |
| 2 | 4 | 30 | 20 | 10 | 100 | 5 |
| 2 | 5 | 3 | 20 | -17 | 289 | 14.45 |
| 2 | 6 | 20 | 20 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 3 | 1 | 17 | 20 | -3 | 9 | 0.45 |
| 3 | 2 | 17 | 20 | -3 | 9 | 0.45 |
| 3 | 3 | 21 | 20 | 1 | 1 | 0.05 |
| 3 | 4 | 20 | 20 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 3 | 5 | 26 | 20 | 6 | 36 | 1.8 |
| 3 | 6 | 19 | 20 | -1 | 1 | 0.05 |
| 360 | chi sq= | 54.2 | ||||
| Using formula | ||||||
| o-e | sq | o-e sq/e | ||||
| 1 | 1 | 10 | 13 | -3 | 9 | 0.692308 |
| 1 | 2 | 15 | 17.3 | -2.3 | 5.29 | 0.30578 |
| 1 | 3 | 30 | 28.7 | 1.3 | 1.69 | 0.058885 |
| 1 | 4 | 30 | 26.7 | 3.3 | 10.89 | 0.407865 |
| 1 | 5 | 15 | 14.7 | 0.3 | 0.09 | 0.006122 |
| 1 | 6 | 20 | 19.7 | 0.3 | 0.09 | 0.004569 |
| 2 | 1 | 12 | 13 | -1 | 1 | 0.076923 |
| 2 | 2 | 20 | 17.3 | 2.7 | 7.29 | 0.421387 |
| 2 | 3 | 35 | 28.7 | 6.3 | 39.69 | 1.382927 |
| 2 | 4 | 30 | 26.7 | 3.3 | 10.89 | 0.407865 |
| 2 | 5 | 3 | 14.7 | -11.7 | 136.89 | 9.312245 |
| 2 | 6 | 20 | 19.7 | 0.3 | 0.09 | 0.004569 |
| 3 | 1 | 17 | 13 | 4 | 16 | 1.230769 |
| 3 | 2 | 17 | 17.3 | -0.3 | 0.09 | 0.005202 |
| 3 | 3 | 21 | 28.7 | -7.7 | 59.29 | 2.065854 |
| 3 | 4 | 20 | 26.7 | -6.7 | 44.89 | 1.681273 |
| 3 | 5 | 26 | 14.7 | 11.3 | 127.69 | 8.686395 |
| 3 | 6 | 19 | 19.7 | -0.7 | 0.49 | 0.024873 |
| 360 | 26.77581 | |||||
3. If there are 9 concordant pairs and 5 disconcordant pairs what is the
value of Goodman & Kruskalís Gamma? (4 marks)
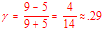
4. Why is the use of a paired t-test preferable to a regular t-test when
comparing the means of paired comparisons? (4 marks)
Since the same objects or persons are used in before and
after much of the error is reduced since the characteristics of the items are
help constant. The key was to talk about a reduction of error
5. What are the 3 types of t-tests?
1 sample, 2 sample, and paired
Quiz 3 Name_____________________________
1. Using the data from the last yearís class quizzes determine lambda. What can
you conclude about the relationship between the 2 quizzes (14 marks)
E1 pick row 3 with value of 16, so error is 50-16=34
E2 col 1 pick row 4 with value of 4 so error is 9-4=5
E2 col 2 pick row 3 with value of 7 so error is 19-7=12
E2 col 3 pick row 2 with value of 7 so error is 17-7=10
E2 col 4 pick row 3 or row 4 with value of 2 so error is 5-2=3
sum of errors for E2 = 5+12+10+3=30
so lambda = (E1-E2)/E2=(34-30)/34=4/34=.12
| Count | ||||||
| quiz 2 classes | Total | |||||
| 4,5,6 | 7,8,9 | 10,11,12 | 13 and 14 | |||
| quiz 1 classes | 4,5,6 | 2 | 3 | 2 | 0 | 7 |
| 7,8,9 | 0 | 4 | 7 | 1 | 12 | |
| 10,11,12 | 3 | 7 | 4 | 2 | 16 | |
| 13 and 14 | 4 | 5 | 4 | 2 | 15 | |
| Total | 9 | 19 | 17 | 5 | 50 |
2. Of the 3 migration models presented in class, which of the distance,
population and simplified gravity model predictions were not statistically
different than the actual migration data?
All of them were statistically different so the answer is
none. (2 marks)
3. You throw a 6 sided die 120 times and you record the number of times you get
each number.
The table of observed values is:
| value | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 |
| frequency | 15 | 14 | 23 | 22 | 25 | 21 |
If you wanted to do a chi square test of the fairness of the die what would
be your expected values? (4 marks)
20 for each value, so a uniform distribution
Quiz 2 Name_____________________________
1. What is the likely effect of increasing the number of categories in a
chi-square test on the probability of finding a significant difference?
As you increase the number of categories it will become
harder to find a difference. (3 marks)
2. If you have a mark that is exactly plus one standard deviation from the mean
and the class has 150 students in it, how many students
received a lower mark than you?(4 marks)
using the rule for a normal distribution we have 68% of students within 1 std
dev. So 150*.68=102 students with scores within 1 std dev
since you are exactly plus one std dev you are the 51st student out from the
mean
since the question asks only about lower there are all the students left of the
mean or 75 students plus the 50 below you that are above the mean so there are
125 students who have a grade lower than you
3. Given the following data, which of the 2 samples has the greatest dispersion.
You must support your decision by using the coefficient of variation. (3 marks)
| Table 1 | ||
| Sample 1 | Sample 2 | |
| 4.1 | 7.7 | |
| 5.3 | 6.7 | |
| 1.3 | 7 | |
| 2.5 | 7.8 | |
| Mean= | Mean= | |
| Std dev= | Std dev= | |
| cv= | cv= |
| sample 1 | sample 2 | |
| 4.1 | 7.7 | |
| 5.3 | 6.7 | |
| 1.3 | 7 | |
| 2.5 | 7.8 | |
| 3.3 | 7.3 | means |
| 1.758787 | 0.535413 | std dev |
| cv | cv | |
| 0.532966 | 0.073344 |
4. If we assume that sample 1 is our observed distribution and sample 2 is
our expected distribution, is sample one significantly different that sample 2?
(6 marks)
| sample 1 | sample 2 | obs-exp | (obs-exp)**2 | /e | |
| 4.1 | 7.7 | -3.6 | 12.96 | 1.683117 | |
| 5.3 | 6.7 | -1.4 | 1.96 | 0.292537 | |
| 1.3 | 7 | -5.7 | 32.49 | 4.641429 | |
| 2.5 | 7.8 | -5.3 | 28.09 | 3.601282 | |
| 10.21836 | chi sq | ||||
| critical value with df=3 and p=,05=7.81 so it is statistically significant | |||||
5. What is the effect of indeterminacy in classification into categories when
using chi-square? (3 marks)
It can create a situation where when forced to place all
items into a set number of classes you can end up with a table that is not truly
reflective of the data. The video gave the case of Mendel and
how his results were thought by some to be too good to
be true
6. Why is knowledge of the mean so important in defining a normal
distribution?(1 marks)
Its one of the 2 parameters required to define it
Quiz 1: Geography 301a, 2005
1. What are the 3 steps in analysis that the video suggested?
1. Producing data
2. Describing data
3. Conclusion from data (3 marks)
2. Name 6 of the case studies provided in the video.
Lightning strikes
human growth hormone
Chesapeake Bay pollution
baseball players salaries
potato chips
manatees
heart attacks
space shuttle
gambling
Hispanic FBI agents
batteries
Salem witchcraft trials
Shakespeareís poem
welfare mothers
childrenís creativity (6 marks)
3. Provide 2 of the 5 preconditions for statistics to be valuable.
1. Can only give answers if the data collection and the
data collected allow such answers
2. User is aware the statistics is just another strategy for finding, patterns
in the data
3. Statistics are based on certain assumptions If those assumptions are not true
the technique can still be applied but significance tests must treated with
caution
4. User is aware that techniques are mathematical models. Reality in all its
complexity cannot be modeled in a useful way. Complex models may imitate reality
but they will be equally complex and therefore not useful. Summarizing data in a
complex way is not a step forward.
5. Data exploration needs to be done before any higher level modeling
(2 marks)
4. What is the preferred method for dealing with missing data?
Listwise deletion (1 mark)
5. What is the weighted mean of following numbers: (please remember false
precision!).
datum weight
1.5 50
50.333 1
6.02 3
22.1 2
| x | w | xw |
| 1.5 | 50 | 75 |
| 50.333 | 1 | 50.333 |
| 6.02 | 3 | 18.06 |
| 22.1 | 2 | 44.2 |
| sum | 56 | 187.593 |
| weighted mean= | 3.349875 | |
weighted mean=3.35 (8 marks)