Quiz No. 11
April 11, 2005
20 marks total
1. Name 4 of the MNEs profiled in the Canadian multinationals presentation
(do not include the Bank of Montreal) . (4 marks)
Massey Ferguson,
Hudson bay Company,
Jetgo,
Nortel,
Alcan,
Research in Motion
2. Name 2 of the 4 organizations or programs that will influence the future
of Canadian multinationals. (2 marks)
NAFTA
Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development (OECD)
Export Development Branch
The Scientific Research and Experimental Development Tax Incentive Program
3. Give a brief review of the development of the Bank of Montreal as a
multinational corporation. (2 marks)
Bank of Montreal:
Created in 1817 by a group of Montreal merchants
Used the best organizational and financial methods of the time
1818 – Opened a branch in New York
1870 – Established a branch in London
4. Currently what’s the largest Canadian multinational (as measured by
revenues)? (2 marks)
Alcan
5. Give 2 of the differences between GATT and the WTO. (2 marks)
GATT is a set of rules; WTO is a permanent institution,
with a secretariat
GATT was applied on a ‘Provisional basis’; WTO commitments are full and
permanent
GATT covered trade in merchandise goods; WTO covers trade in merchandise,
service and intellectual property
WTO dispute method is smoother and faster.
6. Give 6 of the 10 benefits listed for the WTO. (6 marks)
1. The system helps promote peace
2. Disputes are handled constructively
3. Rules make life easier for all
4. Freer trade cuts the costs of living
5. It provides more choice of products and qualities
6. Trade raises incomes
7. Trade stimulates economic growth
8. The basic principles make life more efficient
9. Governments are shielded from lobbying
10. The system encourages good government
7. What are some of the criticisms leveled against the WTO? (2 marks)
Poverty, Inequality, Access, Unfair Trade Barriers,Trade
and Development, Democracy
Quiz No. 10
April 3, 2006
20 marks total
1. What area of the world has the greatest potential for LNG production?
Russia and Iran (2 marks)
2. What are the 4 steps in a country must do to make LNG available to the
market? (4 marks)
Exploration to find natural gas (usually found during
searches for oil)
Liquefaction to convert natural gas into a liquid state so that it can be
transported
Shipping the LNG in special purpose vessels
Storage and Regasification
3. What country has the greatest demand for LNG?
Japan(2 marks)
4. What are the 3 general barriers to increasing the supply of LNG? (3 marks)
Land infrastructure
Pipeline infrastructure
The financial environment
5. Name 3 companies cited in the Alberta oil sands presentation that have
interests in the oil sands. (3 marks)
Shell Canada
Chevron
Esso Imperial oil
Suncor
Texaco
Syncrude
Petro-Canada
Suncor
Sunoco
6. What are the 3 main reasons for rapid development of the oil sands? (3
marks)
More accessible markets
Reduction in supply costs
Recent high crude oil prices
7. What are the 2 basic extraction methods for oil sands? (2 marks)
Surface mining
in situ
8. Presently, to what country are Canadian oil sands oil primarily exported?
(1 mark)
USA
Geography 372b
Quiz No. 9
March 28, 2006
20 marks total, questions 1 to 5 are 2 marks each
1. What is the Zhongguancun Science and Technology Park in Beijing?
China’s Silicon Valley
2. What is the number of China’s cell phone users?
170 million users and growing
3. What is the biggest advantage do local Chinese cell phone manufacturers
have?
They know the local market
4. What is the most popular American brand in China?
KFC with 750 outlets
5. Where has the majority of FDI gone in China (geographically speaking)?
The coastal cities
6. Provide 3 of the promises pledged for the creation of NAFTA (3 marks).
Creation of the world’s largest
market
Export growth
Job creation
Higher living standards
Reduced distortions of trade
Streamlined environmental standards across borders
Protection for basic worker rights
7. Provide 2 of the objectives of NAFTA (2 marks).
Eliminate barriers to trade
Promote fair competition
Increase investment opportunities
Protection on intellectual property rights
Create efficient procedures for implementation of the
agreement
Establishment of the framework for further integration
8. Give the name of 3 of the major TNCs in the agribusiness sector. (3 marks)
Monsanto
Cargill Inc.
DuPont Agriculture and Nutrition
Dow Chemical and Dow AgroSciences
Syngenta
ConAgra
Archer Daniels Midland (ADM)
9. Define agribusiness. (2 marks)
A generic term that refers to the various businesses
involved in food production:
Seed Supply
Farming
Agrichemicals
Farm Machinery & Technology
Wholesale & Distribution
Geography 372b
Quiz No. 8
March 21, 2006
18 marks total
1. Who owned the majority of the major production plants at the end of the 20th
century in China?
The state (3 marks)
2. What was the ‘Iron Rice Bowl’?
Guaranteed employment with the state taking care of you
(3 marks)
4. What was the major problem facing the state enterprises in the late 1980 and
early 1990s?
Too much debt and no demand for their products (3
marks)
5. Give 3 of the motivations behind Chinese firms’ foreign acquisitions. ( 3
marks)
Seeking new markets
purchasing expertise and technology
improving the Chinese economy
brand reputation
securing resources
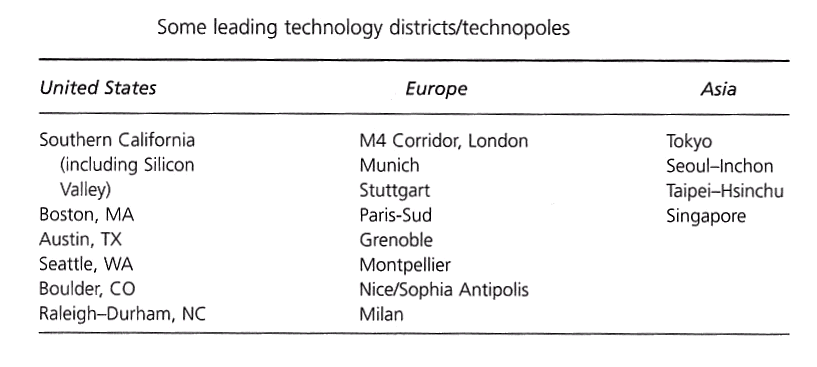
6. Name 3 high technology clusters (in terms of geographic location). (3 marks)
7. What is the Going Out/ Go Out Policy?
Chinese gov’t plan to create 30-35 globally competitive
companies (3marks)
Geography 372b
Quiz No. 7
March 14, 2006
20 marks total
1. What and where is Hyderabad?
High tech center in India (2 marks)
2. What technology had the greatest decline in real prices on an annual basis?
Computers (2 marks)
3. What is Fordism?
the development of the assembly line
(2 marks)
4. What was the significance of the US Supreme Court case DIAMOND v. CHAKRABARTY,
447 U.S. 303 (1980)?
Live organisms can be patented (4 marks)
5. What did the Canadian Supreme Court rule regarding the patenting of living
organisms?
You can’t patent them.
(2 marks)
6. Label the 5 stages in the following figure.
(5 marks)
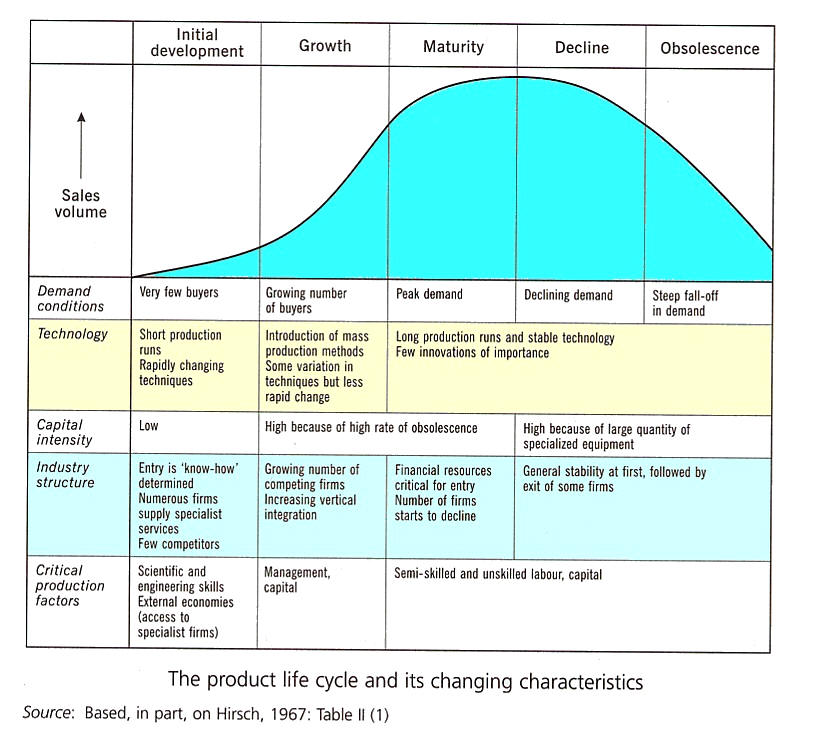
7. Fill in the curve in the second figure (3 marks)
Geography 372b Name________________________
Quiz No. 6 Student Number:________________________
March 7, 2006
20 marks total
1. What is the principle objective of the corporation?
Growing large sustainable profits (3 marks)
2. What was the original purpose of a corporation?
An association chartered by a state to perform a specific
function.
Had a limited life and could not do anything not specified in the corporate
charter (3 marks)
3. What is the legal status of a corporation now?
It’s a legal person but a special kind of person with no
moral conscience.
By law they are concerned only with the interests of its shareholders (2
marks)
4. What institution in the United States granted corporation the right to be a
legal person?
The U.S. Supreme Court ruled on this question in the 1886
case Santa Clara County v. Southern Pacific Railroad. (3 marks)
5. The film: The Corporation, diagnosed corporations as having what type of
psychological condition?
Psychopathic (2 marks)
6. What are the top 2 sectors of the world economy for R & D spending?
Computing and electronics, health (2 marks)
7. Define innovation (as defined by the UN).
Innovation means the introduction of new products,
processes or services into the market (2 marks)
8. What is nanotechnology?
Covers objects 1 to 100 nm(1 marks)
9. At the world regional scale, the largest internet bandwidth connects what 2
regions? (2 marks)
E North America and Western Europe
Geography 372b
Quiz No. 5
February 21, 2006
20 marks total
1. What are the 4 types of technological change? (4 marks)
Incremental innovations
Radical innovations
Changes in the technology system
Impact on several existing parts of the economy
Changes in the techno-economic paradigm
Large-scale revolutionary change
2. What are Kondratieff waves?
The waves supposedly can be found at both the global and
national scales of analysis. They last about 50 years and are divided in half,
with an initial period of strong growth, or upswing, followed by stagnation or
downswing.
(2 marks)
3. Name 6 of the 10 characteristics associated with a techno-economic paradigm?
(6 marks)
Key industries
Infrastructures
Newly emerging industries
Productivity principles
Lead economies
New forms of business organization
Labour relations
Regulation
R&D organization
new location principles
4. What, if anything, did the film Cola Wars reveal about the conduct of
international business? (8 marks)
Geography 372b
Quiz No. 4
February 14, 2006
20 marks total
1. What region of the world has the highest volume of intraregional trade? (1
marks)
Western Europe
2. What was the impact of NAFTA on investment in Northern Mexico, particularly
in the border region?
Investment and establishment of branch plants greatly
increased (2 marks)
3. What is Calpers?
California public employees pension plan (1 mark)
4. Where did ‘contagion’ start?
Thailand, 1997 (1 mark)
5. What are the 2 major components of the Japanese economy?
The domestic market portion which is relatively
uncompetitive and the export oriented one that is very competitive (1
mark)
6. What was Long Term Capital Management’s role in the global financial crisis
of the 1990s?
It was a US fund that was a major player in most financial
markets. The consequences of its failure were uncertain but it was felt it would
be very serious. It appeared that it would fail and was rescued by a consortium
of US banks. (2 marks)
7. What 3 areas of the world have the highest levels of merchandise exports? (3
marks)
North America, Western Europe, SE Asia
8. What country has the world’s largest trade deficit? (1 marks)
US
9. What are the features of an industry that would create a high probability
that it would experience out-sourcing? (6 marks)
No face to face contact required
High information content
The work process is telecommunicable and internet enabled
High wage differentials with similar occupations in destination country
Low set-up barriers
Low social networking requirements
10. What are the 4 stages of a firm’s participation in offshoring? (2 marks)
Bystanders
experimenters
committeds
full exploiters
Quiz No. 3
January 31, 2006
20 marks total
Part 1
Wal-Mart video (2 marks each)
1. What’s the importance of bar-codes on items for Wal-Mart?
Provides sales information, stock inventory
2. What’s the difference between ‘push’ production to ‘pull’ production?
Push is when the manufacturer produces products and then
tries to get retailers to take them, pull is when the retailer tells the
manufacturer what to produce
3. How are negotiations between Wal-Mart buyers and manufacturers conducted?
They meet in Bentonville Ark in a little room. The buyer
knows everything about the manufacturers costs and tells them what Wal-Mart will
pay, it is typically less than the previous year
4. What 2 factors did Wal-Mart take advantage of in its drive to become one of
the world’s largest firms?
Rise of communication technology
Explosion of the global economy
5. What is ‘creative destruction?
More efficient forms of production destroy less efficient
means
Part 2
Give 4 of the 9 mechanisms of resource substitution? (4 marks)

5. What is territorial embeddness? (3 marks)
The concept that economic activity or a firm is
conditioned by the characteristics of the territory it inhabits. This may
include political, social and economic conditions within the territory
6. Who is Ron Martin? (2 marks)
Critic of Krugman who says geographers have already done the studies that
economists are undertaking
7. Who is Paul Krugman?
Economist who is a proponent of ‘new economic geography’
as practiced by economists (1 marks)
Quiz No. 2
January 24, 2006
20 marks total
Part 1
Commanding Heights part 2 (2 marks each)
1. What was the ‘Iron Curtain’?
The sealed borders of Eastern Europe
2. What propped up the failing Soviet economy in the 1980s?
The oil and gas industry with its exports
3. What was dependency theory?
If you want to develop you need to put up trade barriers
and develop internally.
Problem is you cut yourself off from investment and innovation. Industries have
no need to be competitive.
4. What is ‘shock therapy”?
In bringing hyperinflation under control you need to do
all the reforms at once. No gradualism. Spelled the death of dependency theory.
Price controls scraped, gov’t spending was slashed, import tariffs were cut,
gov’t budgets were balanced
5. Why didn’t Gorbachev’s attempt to follow China’s pattern of liberalization
work?
Russia is 80% urban with vast bulk of economy in industry,
while China is 80% rural with predominately a peasant based economy. You can’t
just open up on the margins in Russia the way it was done in China. The nonstate
sector was only 1% of the economy.
6. Who was Deng Xiaoping?
Chinese leader who started market reform in China.
7. What did Peron, Castro and Allende have in common?
All were radical leaders who were suspicious of capitalist
economic approach
Part 2 (2 marks each)
8. Who has the top global brand in terms of value and recognition?
Coca cola
9. What economic sector received the bulk of foreign direct investment (on a
world scale) in 1914)
Natural resources (55%)
10. All production process have what 4 basic core operations?
Inputs
Transformation
Distribution
Consumption
Geography 372b
Quiz No. 1
January 17, 2006
20 marks total
1. What role did the Dissenters play in the industrialization of Great Britain
(4 marks)
Set up academies that taught practical subjects
discovered how to purify coal into coke
engineered paved roads
introduction of a canal system
steam power
introduction of the railways
Commanding Heights questions (2 marks each)
2. What 2 political leaders popularized and led the movement of governments away
from state ownership and excessive regulation of industry?
Thatcher and Reagan
3. Who was John Maynard Keynes?
Believed in government intervention in economy. Was
influential for most of 20th century. Inventor of macroeconomics
4. Who was Friedrich von August Hayek?
Believed gov’t was a threat to freedom. Economy should be
left alone. Ideas weren’t accepted until very later in his life. Saw inflation
as a major evil, opposition to inflation was a cornerstone of this view of
economics
5. What was The General Theory of Employment, Interest and Money?
Book by Keynes in the 1930s that outlined how govt might
intervene in the economy to improve its functioning. Gov’t should spend against
the wind. Spend in low times build surpluses in good times.
6. What are the commanding heights?
Major forms of enterprise such as steel, railways, mining
7. What union’s strike did the United Kingdom’s government
break that started the process of privitization?
Coal miners
8. What was the major glamour stock of the 1920s?
RCA
9. Who introduced the use of central planning of a nation’s economy?
Stalin